Is your team tired of juggling customer support tickets while struggling to keep up with growing order volumes? In today’s ecommerce landscape, fast, personalised, and efficient customer service isn’t just a luxury—it’s a necessity. AI-powered support, like Gorgias' AI Agents, is transforming the way ecommerce businesses are engaging with customers, turning everyday interactions into revenue-driving opportunities.
The Challenges of Ecommerce Customer Service
Running an ecommerce business comes with its fair share of customer service headaches. Brands often struggle with:
- Burnout among support teams – Your agents are overloaded with repetitive questions like “Where is my order?” and “Can I change my shipping address?”
- Rising customer expectations – Shoppers expect instant answers and personalised service, but scaling support is expensive.
- Omnichannel overload – Managing customer messages across email, chat, social media, and SMS can quickly become chaotic.
- Scalability issues – As your business grows, so does the volume of inquiries, making it difficult to maintain a high-quality support experience.
AI-powered customer service is emerging as the solution to these challenges.
Why AI Agents Are a Game-Changer for Ecommerce Support
Traditional customer service is often tied to business hours, reactive, and expensive to scale. AI Agents can change the game by delivering instant responses, 24/7 availability, and intelligent conversations tailored to your customers’ needs. But what sets Gorgias apart is its ability to do more than just answer basic questions—it acts as a powerful sales and customer experience tool.
Here’s how AI Agents can elevate your eCommerce store:
- Instant, 24/7 Customer Support – No more long wait times. AI-powered agents handle high volumes of queries instantly, improving response times and customer satisfaction.
- Personalised Shopping Experiences – AI can analyze customer data in real time to suggest products, offer discounts, and upsell complementary items based on browsing behavior.
- Seamless Order Management – Customers can track orders, request returns, and get updates without waiting for a human agent.
- Automated Upselling & Cross-Selling – AI-powered recommendations increase average order value by suggesting relevant add-ons or upgrades.
- Reduced Support Costs – Automating routine inquiries frees up human agents for complex cases, improving efficiency while keeping costs low.
An Example
Imagine a customer browsing your store at midnight, unsure whether a product is the right fit. Instead of waiting until morning for a response, an AI Agent immediately recommends the perfect item, offers a discount, and secures the sale—while you sleep. This is the power of AI-driven customer support.
With Gorgias you can make this a reality. Easily integrate their AI Agent with your relevant ecommerce apps and then get it to perform actions on your behalf right from the Gorgias platform.
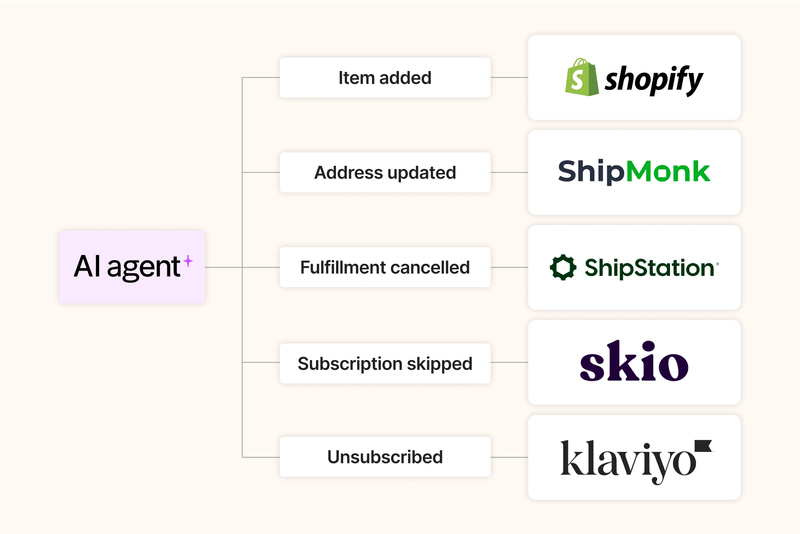
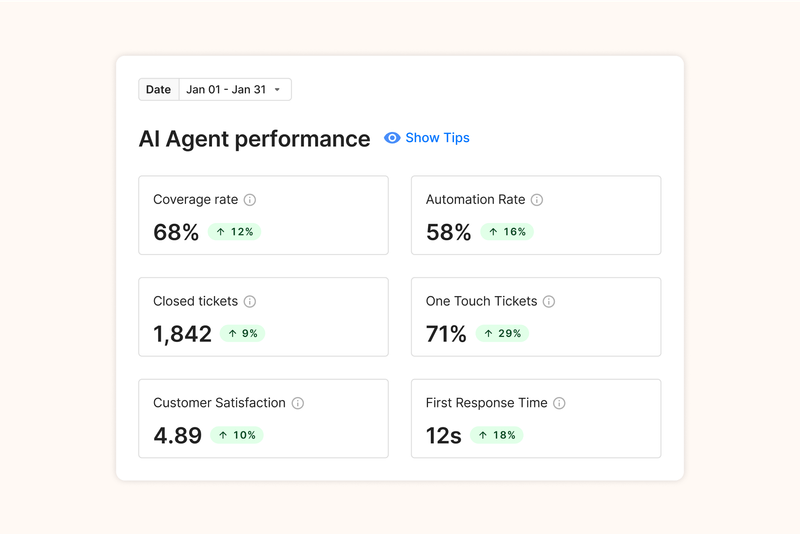
Your Customer Service teams can then track the AI Agents' performance to see how it is going.
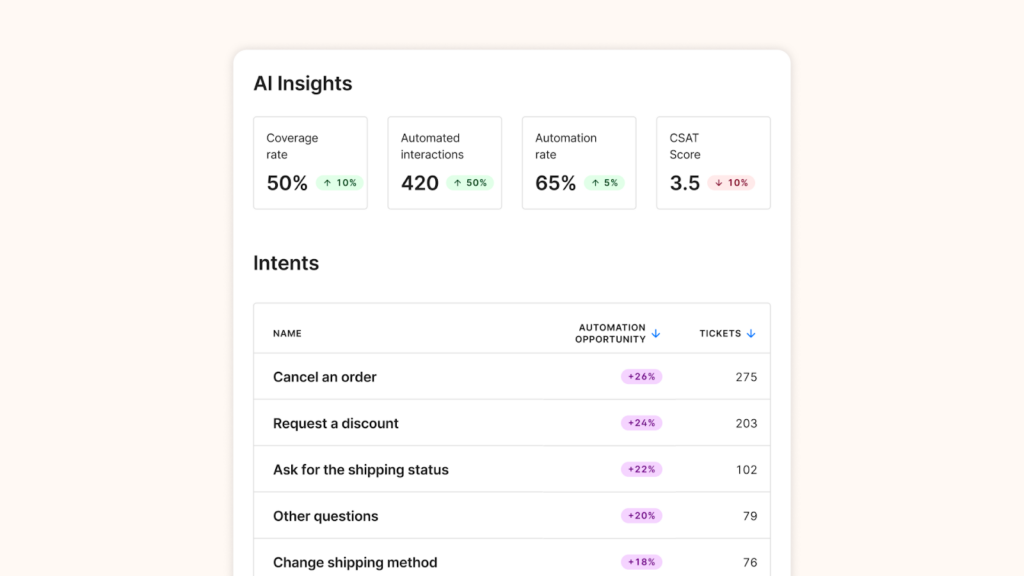
With the Gorgias AI Insights dashboard it can show you where further automations, optimisation or adjustments need to be made.
Why Now is the Time to Embrace AI in Customer Service
With peak shopping events like BFCM (Black Friday Cyber Monday) and festive season sales driving a surge in customer service inquiries, now is the ideal time for ecommerce businesses to strengthen their support operations in preparation for the end of the year. A well-optimised, automated system working alongside human agents ensures a seamless shopping experience while minimising customer frustration during high-traffic periods.
Ask yourself:
- Is my customer service team overwhelmed by repetitive requests?
- Am I missing revenue opportunities due to slow response times?
- Can I scale my support operations efficiently without increasing costs?
- Do I need to convert more customers online and make more sales?
If the answer is yes to any of these, it’s time to review, reorganise, and optimise your customer support strategy, set-up and resourcing.
How Digital Mavens Can Help
As an official Gorgias Partner, Digital Mavens ensures a seamless implementation of Gorgias’ customer service solutions for your e-business. If you're looking to leverage AI-powered agent automation, we will strategically integrate it to enhance customer interactions, elevate your support team's impact, and drive increased sales.
Here’s what we offer:
- Gorgias Helpdesk Set-up & Integration – Seamlessly connecting Gorgias Helpdesk with your Shopify store, CRM, email, chat, social and support channels.
- Gorgias Automate Set-up, Training & Optimisation – Ensuring the AI Agent learns your brand voice, product knowledge, policies, customer intent and provides accurate responses and actions.
- Gorgias Convert Set-up for Sales-Driven Automation – Implementing AI flows and proactive chat that engage customers in real-time and can turn customer queries into upsell opportunities.
- Ongoing Support & Optimisation – Regular monitoring and fine-tuning to improve agent performance over time.
Let’s Future-Proof Your Customer Service
With Gorgias' suite of AI-powered customer support products, you’re not just answering questions and dealing with issues—you’re creating a seamless shopping experience that automates customer responses, saves time, reduces costs, converts more customers, drives more sales and builds higher customer satisfaction.
Ready to future-proof your customer service? Contact our Chief Maven, Kingston Lee-Young for a chat about your customer service business and challenges.
The B2B ecommerce landscape is evolving fast, and if you’re a B2B business owner, CEO, Sales Director, Marketing Director or IT Director, it’s time to ask yourself a critical question: Is your B2B ecommerce strategy and set-up ready for 2025?
By 2025, Gartner predicts that 80% of B2B sales interactions will occur in digital channels. With the rapid shift to digital-first experiences, the time to future-proof your ecommerce strategy is now.
Why Digital-First and B2B Ecommerce is the Future of B2B Sales
Digital transformation is no longer optional, it’s a business imperative. The B2B buyer demographic is changing, and so are their expectations.
Millennials and Gen Zers are Dominating B2B Buying. A generational shift is underway in B2B buying. In 2023, 71% of B2B buyers were born after 1980, according to Forrester’s Buyers’ Journey Survey. These digital natives expect seamless, digitally rich purchasing experiences, similar to what they encounter in B2C ecommerce.
Self-Service is the New Standard. Gartner Sales Survey found that 83% of buyers prefer to manage orders and accounts online, and many want self-service tools throughout their buyer journey. Offering intuitive, self-service options is no longer a competitive advantage—it’s the minimum.
Additionally, today’s buyers are conducting significant research before even reaching out to a sales representative. They rely on comprehensive, easily accessible product information, technical specifications, and peer reviews to guide their decisions. Businesses that make this data readily available online gain a substantial advantage in influencing purchase intent and closing the sale.
6 Key Trends to Watch in B2B Ecommerce for 2025
- The Rise of Omni-channel
Buyers are increasingly leveraging digital technologies earlier in the sales process. An omnichannel strategy (combining web, mobile, email, and social media) will play an important role in influencing purchasing decisions. - Hyper-Personalisation is Taking Over
Traditional account-based marketing is giving way to hyper-personalisation, where messages are tailored to individual decision-makers using data-driven insights. Expect this to become the gold standard for B2B marketing in 2025. - Social Media as a Sales Channel
Social media platforms are no longer just for brand awareness; they’re becoming integral to B2B sales strategies. Companies are using LinkedIn, Instagram, and even TikTok to nurture leads and close deals. A well-executed social selling strategy can position your business as a trusted advisor in your space. - Dynamic Pricing Strategies
Static pricing models are being replaced by flexible, data-driven pricing strategies that reflect real-time demand, customer segmentation, and competitive insights. - On-Demand Product and Service Data
B2B buyers expect comprehensive product and service information to be available online 24/7. Investing in a robust B2B ecommerce platform, like Shopify Plus, and setting up customer-specific digital catalogues is essential. This not only helps improve the buying experience but also fosters stronger customer loyalty through transparency and accessibility. - Tech-Savvy Buyers Want More
B2B buyers are increasingly leaning into digital tools, from AI-driven chatbots to interactive product configurators. Enhancing the digital experience can help your business stand out in a crowded marketplace.
Is Your B2B Ecommerce Strategy Ready?
In 2025, the key to success lies in staying agile, innovative, and customer-centric. Here are three steps to get your B2B ecommerce strategy ready for 2025:
- Evaluate Your Platform: Is your current ecommerce platform scalable, secure, and integrated with your CRM and ERP systems?
- Embrace Data-Driven Decisions: Use analytics to identify customer behaviours and preferences, enabling hyper-personalised experiences.
- Invest in Technology: From AI-driven recommendations to dynamic pricing models, invest in technologies that enhance the customer journey.
Let’s Talk About Your B2B Ecommerce Strategy
At the Digital Mavens, we specialise in helping B2B businesses optimise their ecommerce platforms and strategies to meet the demands of tomorrow’s buyers. If your current setup isn’t delivering the results you need, it’s time for a change.
Ready to future-proof your B2B ecommerce? Contact our Chief Maven, Kingston Lee-Young for a chat about your business and challenges.
With just under 4-months until Black Friday and Cyber Monday (BFCM), and the start to the traditional Christmas Shopping period, now is the time to ensure your ecommerce platform is ready to handle the end-of-year shopping surge. If your online business is experiencing any of the following issues, it might be time to consider an ecommerce migration:
- Lost Sales Due to Poor Onsite User Experience: Are customers leaving your site frustrated because it’s hard to navigate, they can’t find the products they want, or it’s difficult to checkout and pay?
- Lack of System Integration: Are your business systems disconnected from your ecommerce site, leading to manual processes that cause inefficiencies and errors?
- Inability to React to Customer Demands: Are you struggling to adapt quickly to customer needs or market trends?
- Untracked Analytics: Without proper analytics, do you know which ads are driving sales or which categories are attracting the right customers?
- Stock and Delivery Challenges: Is managing inventory, fulfilling orders, and organising deliveries becoming a nightmare?
- Customer Service Issues: Are customer inquiries slipping through the cracks due to inadequate support tools?
- Missed Opportunities for Customer Retention: Are you unable to nurture customers with email campaigns that encourage repeat purchases? Do you know who your best customer segments are?
- Performance Problems: Are slow load times and technical glitches costing you sales?
- Slow Development Cycles: Does it take months, rather than weeks or days, to deploy essential updates, fixes, or new functionality?
- Improper Site Setup: Is your site not optimised for performance, security, or user experience?
If these challenges sound familiar, it’s time to seriously consider migrating to a different ecommerce platform or enhancing your current one.
Why We Recommend Shopify as the Best Ecommerce Platform
At Digital Mavens, we’ve worked with a wide range of ecommerce platforms, including BigCommerce, WooCommerce, Salesforce Commerce Cloud, Magento, and UltraCommerce. From our extensive experience, we can confidently say that Shopify is the best choice for most businesses looking to build or scale their online presence. Here’s why:
1. Ease of Use
If a platform is easy-to-use, you’re more likely to leverage its full potential. Shopify’s user-friendly interface makes managing and updating your e-store simple. You can easily modify functionality and features without requiring a large team or technical expertise. Plus, there are plenty of themes and apps to choose from, saving you from having to build everything from scratch. Shopify also simplifies the checkout process and is constantly innovating to improve user experience.
2. Speed of Change
Shopify allows you to implement changes quickly. Whether you’re launching a new product or responding to market demands, you can do it in days, not months - sometimes even minutes. With Shopify, your ecommerce manager can handle many updates in-house, reducing the need to outsource to technical support.
3. Managed Site Performance
With Shopify, you don’t have to worry about uptime, load balancing, or scalability - Shopify handles all of this for you. This ensures your site performs optimally, even during peak traffic periods like BFCM and other promotional periods.
4. Security and Compliance
Shopify is PCI DSS compliant, offering top-notch security for payment processing and customer data. This protects your business from breaches and ensures customer trust. Shopify also enables automated processes to reduce chargebacks and prevent fraudulent purchases.
5. Seamless Integration
Shopify easily integrates with various business systems and platforms, including ERP, WMS, OMS, customer service tools, and analytics. This interconnectedness streamlines your operations and enhances efficiency.
6. Focus on Your Business
With Shopify handling the technical heavy lifting, you can focus on what really matters: driving sales, finding and engaging customers, optimising your product catalogue, and growing your profit margins.
Considering a Move to Shopify? Here’s What You Need to Know About Ecommerce Migrations
If you’re thinking about switching from your current ecommerce platform to Shopify or Shopify Plus, we’re here to help. Ecommerce migrations can seem daunting, but with the right planning and execution, it can be a smooth process. Here are some of the key steps to consider:
1. Your Ecommerce Migration Timeline
Most Shopify migrations take about 3 months. For example, we recently completed a comprehensive migration for Toys R Us in just three months. This involved migrating from OSCommerce to Shopify Plus, redesigning and building the store, integrating with MYOB, installing multiple feature apps, migrating email marketing from MailChimp to Klaviyo, transitioning customer service from OSTicket to Gorgias, handling data migration, and conducting thorough testing.
2. Evaluating Your Current Needs
Assess what functionality, features, and requirements are essential for your new Shopify store. Identify what’s missing from your current platform that you need in your new Shopify setup.
3. Understanding Your Customers’ Needs
What do your customers want for an enjoyable and repeatable shopping experience? Ensure your new onsite experience is designed with them in mind, enhancing their journey, solving their shopper missions and encouraging purchases.
4. Supporting Your Staff
Evaluate what your internal team needs to do their jobs efficiently and effectively. The right tools can positively impact productivity, efficiency, and job satisfaction. Adding Shopify apps could help to improve your internal processes.
5. Data Migration
Carefully plan the migration of product data, customer records, historical orders, financial data, and marketing assets. This step is crucial to ensuring a seamless transition to the new Shopify store and the ability to make sales once launched.
6. Store Design, Customisation, and Configuration
Tailor your Shopify store to reflect your brand, align with your marketing and sales objectives, and support your operational setup and business goals. Migrations onto a new ecommerce platform are a great opportunity to ensure your new store design prioritises user experience and scalability, allowing for future growth and adaptability as your business evolves.
7. Integration with Business Systems
Review all your ecommerce platform integrations with your business systems, like ERP, WMS, OMS, customer service platforms, and analytics tools. Are they all integrated? If not, take the migration opportunity to bring everything together with your ecommerce migration to Shopify. Correct integration will streamline your operations, reduce manual processes, and provide real-time data insights that can drive more informed decision-making and enhance overall efficiency.
8. Testing and Launch
Rigorous testing is essential before going live with your new Shopify store. Make sure you have allowed time to test, have documented processes, and have a cross-functional team to test every part of the process before going live. Consider testing across different devices and browsers to ensure consistent performance and usability, make real-life orders and refunds, and have a contingency plan in place to quickly address any unexpected issues post-launch.
9. Ongoing Optimisation
Post-launch, make sure to continue monitoring and optimising your new Shopify store to adapt to customer feedback, behaviours, sales results and changing market conditions. At Digital Mavens, we don’t just launch and leave; we can also provide ongoing support to ensure growth and success until you’re confident enough to build your own internal team.
Need More Information or Advice Before Migrating? Let’s Chat
If you’re ready to explore migrating to Shopify but need more advice or information, we’d love to help. Schedule a time to Speak to the Chief about your ecommerce needs and challenges. With our expertise, we can ensure your migration is smooth and that your new Shopify store is set up for success - just in time for BFCM and end-of-year sales opportunities.
Let’s make sure your business is ready to thrive this season and beyond.
Find Out More About How We Can Help You With Your Ecommerce Growth
Checkout out our ecommerce services, Ecommerce Copilot Program and Shopify Virtual Shopping pages.
